Heart Failure in Cardiac Amyloidosis: Understanding HFpEF and HFrEF
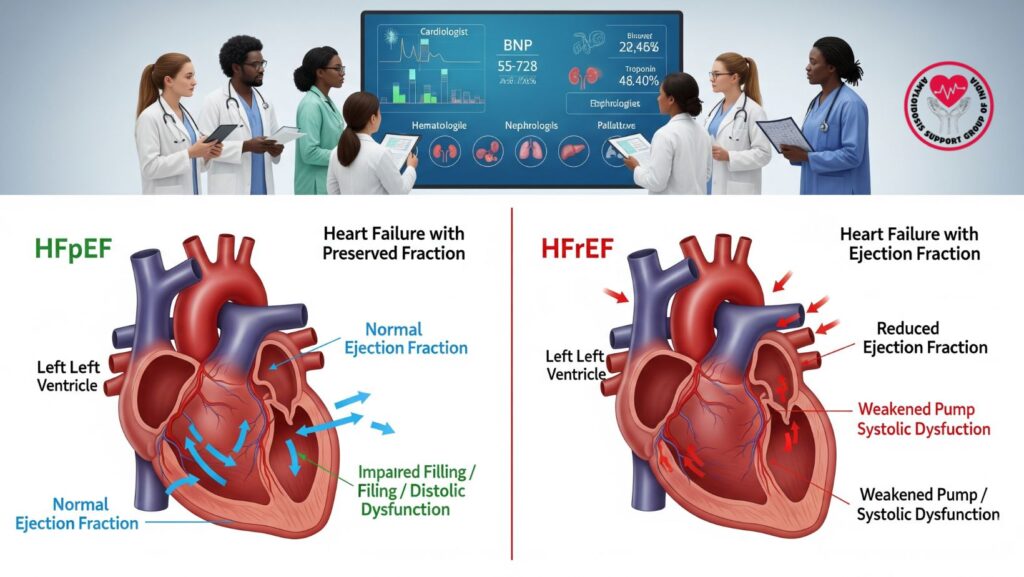
Table of Contents
1. Introduction
Cardiac amyloidosis (CA) is a severe expression of systemic amyloidosis where amyloid proteins deposit in the heart, causing structural and functional derangements. The most common cardiac manifestation is heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), but others present with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF).
Knowledge of the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of HFpEF and HFrEF in CA is important to enhance survival and quality of life. This review is an extensive overview for doctors, caregivers, and patients.
2. Pathophysiology of Cardiac Amyloidosis
Amyloid fibrils, made mostly of immunoglobulin light chains (AL type) or transthyretin (ATTR type), accumulate in the myocardium. This accumulation results in:
- Increased ventricular wall thickness without dilation
- Reduced myocardial compliance → diastolic dysfunction
- Conduction abnormalities → arrhythmias and AV block
- Myocardial ischemia due to microvascular involvement
HFpEF vs HFrEF in CA:
- HFpEF: More common, characterized by normal ejection fraction but impaired diastolic filling due to stiff ventricles.
- HFrEF: Less common, occurs when amyloid infiltration progresses to systolic dysfunction, lowering ejection fraction.
3. Clinical Features
3.1 Symptoms
Patients may present with:
- Dyspnea on exertion (most common)
- Peripheral edema
- Orthopnea and paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
- Fatigue and exercise intolerance
- Palpitations or syncope if arrhythmias develop
3.2 Physical Examination
- Jugular venous distension
- S3 or S4 gallop
- Peripheral edema
- Hepatomegaly or ascites in advanced cases
Key point: HFpEF patients may appear “normal” on EF measurement but exhibit severe symptoms due to stiff ventricles and elevated filling pressures.
4. Diagnostic Evaluation
4.1 Echocardiography
- Increased ventricular wall thickness
- Diastolic dysfunction
- Speckled or granular myocardial appearance
- EF: Preserved in HFpEF, reduced in HFrEF
4.2 Cardiac MRI
- Late gadolinium enhancement indicating amyloid infiltration
- Assessment of ventricular mass and fibrosis
4.3 Biomarkers
- BNP/NT-proBNP: Elevated in both HFpEF and HFrEF
- Troponins: Indicate myocardial injury
4.4 Electrocardiography
- Low voltage in limb leads
- Pseudoinfarct patterns
- Conduction abnormalities
4.5 Tissue Biopsy
- Endomyocardial biopsy is definitive
- Typing amyloid (AL vs ATTR) guides therapy
5. Management of HFpEF in Cardiac Amyloidosis
HFpEF management focuses on symptom relief and prevention of complications:
5.1 Diuretics
- Loop diuretics and aldosterone antagonists for volume control
- Avoid aggressive diuresis → hypotension and renal dysfunction
5.2 Rate Control & Rhythm Management
- Beta-blockers are used cautiously
- Amiodarone for atrial fibrillation
- Pacemakers or defibrillators for conduction abnormalities
5.3 Supportive Care
- Low-salt diet
- Fluid restriction
- Exercise as tolerated
- Multidisciplinary support (cardiology, nephrology, nutrition, palliative care)
5.4 Disease-Targeted Therapy
- AL amyloidosis → chemotherapy
- ATTR amyloidosis → tafamidis, diflunisal, or RNA therapies
6. Management of HFrEF in Cardiac Amyloidosis
HFrEF management addresses systolic dysfunction while considering amyloid-specific limitations:
6.1 Pharmacologic Therapy
- Standard HFrEF drugs (ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers) may not be tolerated
- Diuretics for congestion
- Take careful consideration of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist use
6.2 Device Therapy
- Pacemaker for AV block
- Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) for the prevention of arrhythmia
6.3 Heart Transplantation
- Reserved in selected advanced cases
- Often used in conjunction with systemic therapy in AL amyloidosis
7. Multidisciplinary Care in Cardiac Amyloidosis
Management should be team-based and include:
- Cardiologists → managing heart failure, monitoring EF and arrhythmias
- Hematologists → treatment of AL amyloidosis
- Neurologists → management of autonomic neuropathy or conduction problems
- Nephrologists → kidney complications
- Nutritionists & Palliative Care → symptom control, quality of life
Benefits: Enhanced survival, organ-specific treatment coordination, and patient quality of life improvement.
8. Prognosis
- HFpEF patients: Severe symptoms but EF is maintained; prognosis is based on organ involvement and response to therapy.
- HFrEF patients: Poorer prognosis with far advanced myocardial infiltration.
- Early diagnosis and prompt systemic therapy initiation greatly enhance outcomes.
9. New Therapies and Studies
- TTR stabilizers (tafamidis, diflunisal) for ATTR amyloidosis
- Gene-silencing therapies (patisiran, inotersen)
- Novel AL therapies: Proteasome inhibitors, monoclonal antibodies
- Research on combined supportive and disease-directed care shows improved HFpEF symptom control
10. Patient Education and Lifestyle
- Adherence to low-salt diet and fluid restriction
- Monitoring weight and blood pressure at home
- Recognizing early signs of fluid overload or arrhythmia
- Engaging in safe physical activity
- Psychological support for disease management of chronic disease
11. Case Example (Optional)
A 65-year-old patient with ATTR amyloidosis had HFpEF:
- Echocardiogram revealed thickened ventricles with normal EF
- BNP was elevated, mild peripheral edema
- Treated with loop diuretics, low-salt diet, and tafamidis
- Multidisciplinary team involved cardiology, nutrition, and neurology
- Outcome: Stabilization of symptoms, enhanced functional ability, delay in the progression to HFrEF
12. Conclusion
Cardiac amyloidosis-related heart failure occurs as HFpEF most often, but HFrEF may occur in end-stage disease. Treatment needs:
- Correct diagnosis with imaging, biomarkers, and biopsy
- Symptom-guided treatment with judicious pharmacologic therapy
- Disease-directed therapy for AL or ATTR amyloidosis
- Multidisciplinary supportive care in centers of excellence
Key Takeaways:
- HFpEF is common; follow diastolic dysfunction closely
- HFrEF reflects severe infiltration and needs careful management
- Early diagnosis and a team approach enhance survival and quality of life

