Table of Contents
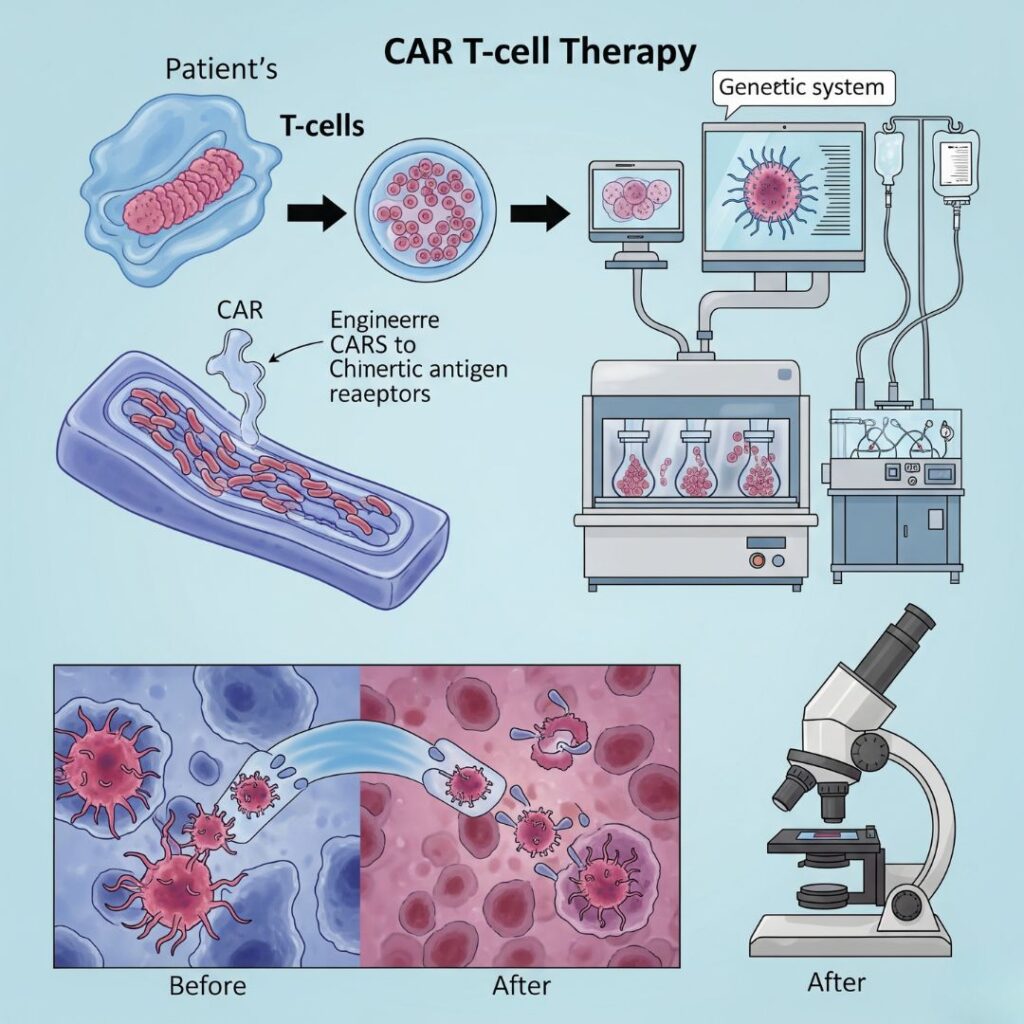
CAR T-cell therapy (Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell therapy) is a ground-breaking type of immunotherapy that employs a patient’s own immune cells to combat cancer—particularly blood cancers such as leukaemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma.
How It Works (In Simple Steps):
- T-Cell Collection:
Blood is withdrawn from the patient, and T-cells (a subset of white blood cells responsible for fighting infection) are isolated. - Genetic Engineering:
In a laboratory, these T-cells are engineered to make chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) on the surface. These CARs enable the T-cells to identify particular proteins (antigens) on cancer cells. - Cell Expansion:
The engineered T-cells are cultured in the lab in large quantities to produce millions of copies. - Infusion Back into Patient:
The engineered T-cells are infused back into the patient’s blood. - Cancer Attack Mode:
Once in the body, CAR T-cells home in on and kill cancer cells bearing the target antigen.
What Cancers Does CAR T-cell Therapy Treat?
As of today, it’s FDA-approved for:
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
- Certain forms of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
- Multiple Myeloma
There are ongoing trials investigating its application in solid tumors as well.
Advantages
- Extremely targeted and personalized
- Can cause long-term remission in patients who failed to respond to other treatments
- A potential choice for relapsed or refractory cancer
Risks & Side Effects
- Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS): Immune overactivation leading to flu-like symptoms
- Neurological problems: Confusion, headache, or seizures
- Risk of infection: Owing to suppression of the immune system
Patients are carefully observed in special treatment facilities.
In Summary:
CAR T-cell therapy is akin to transforming your body’s T-cells into “guided missiles” that find and destroy cancer cells. It is one of the most promising breakthroughs in personalized cancer treatment and immunotherapy now.
(FAQs) About CAR T-Cell Therapy
1. What is CAR T cell therapy?
CAR T-cell therapy is a form of immunotherapy in which a patient’s own T-cells are genetically engineered to identify and kill cancer cells. Such modified cells are referred to as Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-cells.
2. What are the kinds of cancer that CAR T cell therapy can treat?
CAR T-cell therapy is presently approved for many blood cancers, including:
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
- Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL)
- Mantle Cell Lymphoma
- Multiple Myeloma (targeting BCMA)
It is not yet generally accepted for solid tumors, but it is being tested in clinical trials.
3. How long does the CAR T cell therapy process take?
The entire process typically takes 3 to 6 weeks, which includes:
- Collection of T-cells
- Genetic modification and expansion of cells
- Chemotherapy before treatment
- Infusion of CAR T-cells
- Monitoring and recovery
4. What are the side effects of CAR T cell therapy?
Common side effects are:
- Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS): Fever, low blood pressure, trouble breathing
- Neurotoxicity (ICANS): Headache, confusion, seizures
- Infections: Secondary to immune suppression
- Low blood counts
Side effects are usually manageable with medication and hospitalization.
5. How successful is CAR T cell therapy?
CAR T-cell therapy has had high rates of remission, particularly in patients who have been resistant to other therapies. Some patients have sustained remission, while others require further therapy.
6. Is CAR T cell therapy a cure for cancer?
CAR T-cell therapy can result in complete remission, but not a sure thing. Some patients stay cancer-free for years, but some relapse. Improved durability is being researched.
7. Can anyone get CAR T cell therapy?
No. Eligibility is based on such things as:
- Cancer type and stage
- General health
- Past treatments
- Availability of target antigen (such as CD19 or BCMA)
A doctor will determine whether a patient is eligible.
8. How much does CAR T cell therapy cost?
Its may cost $350,000 to $500,000+ USD, depending on the nation, hospital, and cancer type. Insurance coverage is variable and financial assistance programs might be an option.
9. What to expect after CAR T cell infusion?
Following infusion, patients are closely monitored for at least 7–14 days (usually in the hospital) for side effects to be controlled. Long-term follow-ups last for a few months or even years.
10. Is CAR T cell therapy globally available?
Although offered in nations such as the USA, UK, Germany, and India, access is restricted by cost, infrastructure, and regulatory clearances. In many countries, clinical trials represent an option for access to the treatment.

